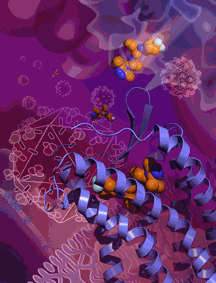
In a long-awaited finding, an international team of scientists using high-brightness x-rays from the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science’s Advanced Photon Source at Argonne National Laboratory has determined the high-resolution atomic structure of a cell-surface receptor that most strains of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) use to gain entry to human immune cells. The researchers also showed where maraviroc, an HIV drug, attaches to cells and blocks HIV’s entry.
“These structural details should help us understand more precisely how HIV infects cells, and how we can do better at blocking that process with next-generation drugs,” said Beili Wu, professor at the Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica (SIMM), Chinese Academy of Sciences. Wu was the senior investigator for the study, which was published online in “Science Express” and in the September 20, 2013, issue of Science.
Both CCR5 and CXCR4 belong to a large family of cell receptors known as G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). (Determination of the structure of a human GPCR, based in large part on research carried out at the Advanced Photon Source, earned the 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.) GPCRs are notoriously hard to produce in useful amounts for structural analysis. With their floppy structures, they are also very hard to coax into the ordered, solid lineups of individual molecules — “crystals” — needed for structure determination by x-ray crystallography.
The study, which focused on the CCR5 receptor, was supported by both U.S. and People's Republic of Chinese research funding agencies. “International collaborations like this one are increasingly needed to solve big problems in science,” said study co-author Raymond C. Stevens, a professor at The Scripps Research Institute in California. “Now that we have both human CXCR4 and CCR5 HIV co-receptor three-dimensional structures, it is likely we will see the next generation of HIV therapeutics.”
The CCR5 receptor is one of the most sought-after targets for new anti-HIV drugs. Although the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)-causing virus was initially discovered to infect cells via another receptor, CD4, researchers found in 1996 that HIV infection also requires a co-receptor — usually CCR5, which sits alongside CD4 on a variety of immune cells.
CCR5’s importance to HIV infection is underscored by the fact that certain genetic variants of it can dramatically raise or lower HIV infection risk, as well as the speed of the disease process after infection. One shortened CCR5 variant, found in about 10% of Europeans, is not expressed at all on immune cell surfaces, and people who produce only this variant are almost invulnerable to HIV infection.
Scientists, therefore, have sought to develop anti-HIV drugs that block the virus from binding to CCR5 or otherwise render the receptor inactive. Yet only a handful of CCR5-inhibiting compounds have been developed so far — and no one knows exactly how they work. “One thing that we’ve lacked is a high-resolution molecular ‘picture’ of the CCR5 receptor structure that we can use for precise drug design,” Wu said.
Eventually, however, with help from insights gained during the CXCR4 project, Wu and her team of students used a novel “fusion partner” molecule that would hold CCR5 proteins together enough to form usable crystals, together with efforts of computational modeling, compound synthesis and cell signaling assays, which led to the structure determination of CCR5.
The resulting crystallography data obtained at the 23-ID-D beamline of the National Institute of General Medical Sciences and National Cancer Institute (GM/CA) structural biology facility at the Advanced Photon Source provided a fine-grained picture of CCR5’s HIV-resistant conformation. The data also revealed maraviroc’s precise binding site on CCR5 — a site from which the drug molecule clearly influences how the receptor works, even though it is separate from the sites on the receptor that are thought to be used by HIV.
The maraviroc binding site is also different from the site used by CCR5’s natural binding-partners, a set of immune proteins called chemokines. Maraviroc (a Pfizer drug sold under the brand name Selzentry® or Celsentri® outside the U.S.), thus appears to work against HIV indirectly — not by physically blocking the virus, but by locking the receptor structure into an HIV-insensitive conformation.
“This study provides knowledge about the interactions between maraviroc and CCR5, a target for anti-HIV therapy that helps us understand how the drug works at the molecular level and could enable further explorations of HIV biology and approaches to improve drugs targeting such interactions,” Said Peter Preusch of the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, which helped fund the research along with the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
Comparison of the CCR5 structure with the previously determined CXCR4 structure also provided hints about an important aspect of HIV evolution during infections. Most HIV infections start by using only CCR5 as a co-receptor for cell entry, but in time the virus often switches its co-receptor usage from CCR5 to CXCR4. That opens up more cell types to HIV infection, and the further spread of the virus inside the body is liable to speed up the disease progression towards full-blown AIDS and death.
The new data suggest that the distinction between CCR5 and CXCR4 as co-receptors for HIV infection boils down to relatively subtle differences in structural shapes and electric charge distributions in the HIV binding region — differences that will be of interest to HIV drug developers.
“Knowing the CXCR4 structure and now the CCR5 structure at this level of detail should accelerate the development of drugs that can block HIV by using both of these co-receptors,” said Wu.
Wu and her colleagues plan to follow up with structural studies of CCR5 and CXCR4 in complex with the HIV envelope protein gp120 and CD4 to obtain even more informative pictures of the process of viral infection.
In addition to Wu and Stevens, contributors to the study were lead author Qiuxiang Tan, and Ya Zhu, Jian Li, Zhuxi Chen, Tingting Li, Limin Ma, Jing Li, Wenru Zhang, Huaiyu Yang, Qiang Zhao, Gye Won Han, Gustavo Fenalti, Vadim Cherezov, and Irina Kufareva.
The original Scripps Research Institute press release can be found here.
See: Qiuxiang Tan1, Ya Zhu1, Jian Li1, Zhuxi Chen1, Gye Won Han2, Irina Kufareva3, Tingting Li1, Limin Ma1, Gustavo Fenalti2, Jing Li1, Wenru Zhang1, Xin Xie1, Huaiyu Yang1, Hualiang Jiang1, Vadim Cherezov2, Hong Liu1, Raymond C. Stevens1, 2,4, Qiang Zhao1, and Beili Wu1, “Structure of the CCR5 Chemokine Receptor–HIV Entry Inhibitor Maraviroc Complex,” Science 341, 1387 (20 September 2013). DOI: 10.1126/science.1241475
Author affiliations: 1Chinese Academy of Sciences; 2The Scripps Research Institute; 3University of California, San Diego; 4ShanghaiTech University
Correspondence: *beiliwu@simm.ac.cn
This work was supported by National Basic Research Program of China grants 2012CB518000 and 2012CB910400; National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant R01 AI100604; National Science Foundation of China grants 31270766, 81161120425, and 81025017; and Shanghai Science and Technology Committee grants 11JC1414800 and 12PJ1410500. Additionally, V.C. and R.C.S. acknowledge support from NIH grant U54 GM094618 (Target GPCR-28); I.K. acknowledges support from U01 GM094612, U54 GM094618, and R01 GM071872.
GM/CA has been funded in whole or in part with Federal funds from the National Cancer Institute (Y1-CO-1020) and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (Y1-GM-1104). Use of the Advanced Photon Source is supported by the U.S. DOE Office of Science under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357.
The Advanced Photon Source at Argonne National Laboratory is one of five national synchrotron radiation light sources supported by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science to carry out applied and basic research to understand, predict, and ultimately control matter and energy at the electronic, atomic, and molecular levels, provide the foundations for new energy technologies, and support DOE missions in energy, environment, and national security. To learn more about the Office of Science x-ray user facilities, visit http://science.energy.gov/user-facilities/basic-energy-sciences/.
Argonne National Laboratory seeks solutions to pressing national problems in science and technology. The nation's first national laboratory, Argonne conducts leading-edge basic and applied scientific research in virtually every scientific discipline. Argonne researchers work closely with researchers from hundreds of companies, universities, and federal, state and municipal agencies to help them solve their specific problems, advance America's scientific leadership and prepare the nation for a better future. With employees from more than 60 nations, Argonne is managed by UChicago Argonne, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science.