This article is based upon the Scripps Research Institute press release, which can be read here.
We are closer to understanding the workings of the intricate molecular mechanism of a metabolic enzyme produced in most forms of life on Earth, thanks to a team of structural biologists from The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) and experiments carried out at two U.S. Department of Energy synchrotron light sources including the Advanced Photon Source (APS) at Argonne National Laboratory.
The finding, published in the journal Science, concerns nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase (TH), an ancient evolutionary enzyme found throughout the animal kingdom as well as in plants and many simpler species. The enzyme is part of a process key to maintaining healthy cells and has also recently been linked to diseases such as diabetes and cancer.
“Despite its importance, TH has been one of the least-studied of mitochondrial enzymes,” said C. David Stout of TSRI, a co-author of the Science paper. “Our new study helps clear up some mysteries by suggesting how the enzyme structure might harness protons and indicating that its two sides are able to alternate functions, always staying in balance.”
In humans and other higher organisms, TH enzymes work within mitochondria, the tiny, double-hulled oxygen reactors that help power most cellular processes.
As a mitochondrion burns oxygen, it pumps protons (hydrogen atoms denuded of their electrons) out of its inner compartment (“matrix”), creating an excess of these charged particles just outside its inner membrane. TH enzymes, which are fixed at one end within this membrane, allow a one-by-one flow of protons back through the membrane within the matrix. This process — which is similar to that which makes ATP, the cell’s universal source of energy — has also been linked to the production of a compound called NADPH, which is crucial for defusing oxygen free radicals to maintain cell health.
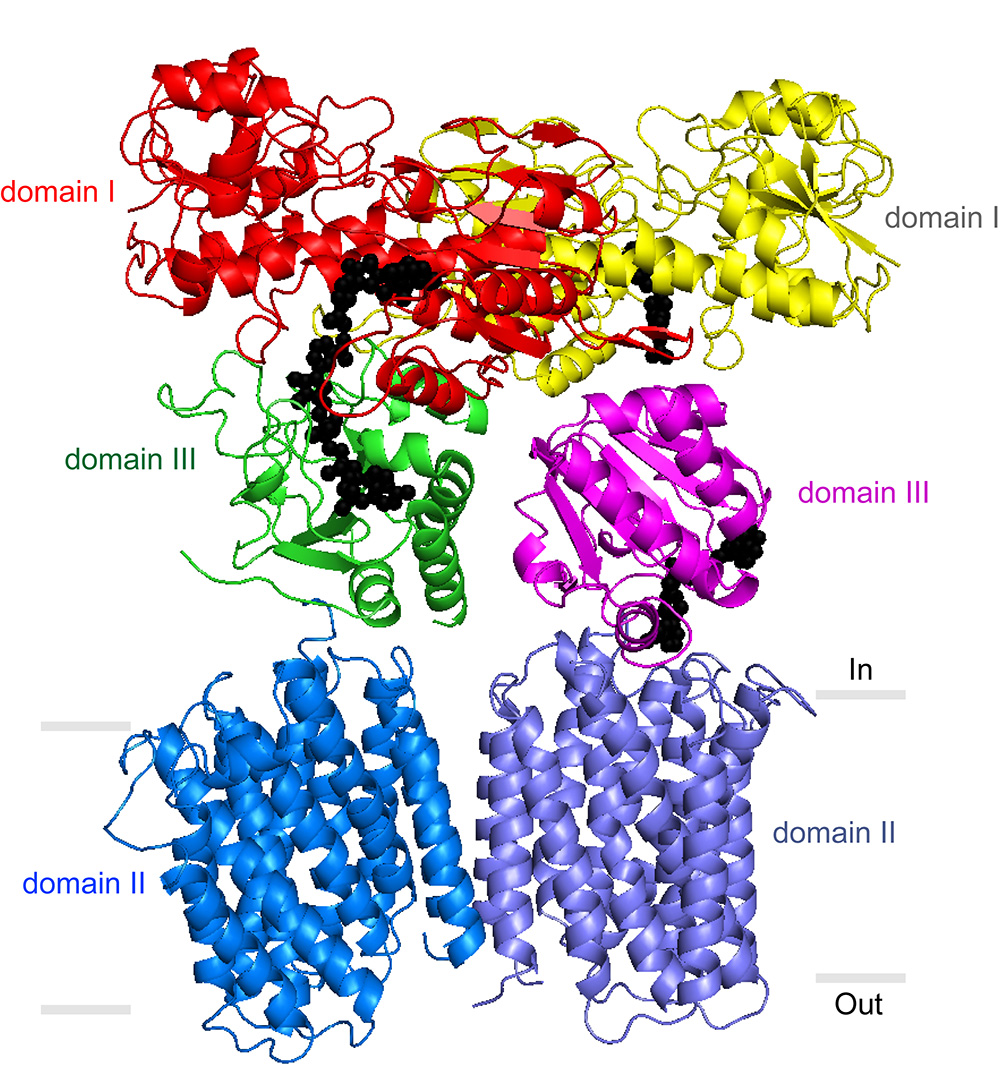
Stout’s laboratory and others have previously described portions of the TH enzyme that protrude from the membrane into the mitochondrial matrix. But a precise understanding of TH’s mechanism has been elusive. In its entirety, the enzyme has an exceptionally loose structure that makes it hard to evaluate using x-ray crystallography, the standard tool for determining the structures of large proteins at atomic-level resolution.
“Key details we’ve been lacking include the structure of TH’s transmembrane portion, and the way in which the parts assemble into the whole enzyme,” said Josephine H. Leung, a graduate student in the Stout laboratory who was lead author of the study.
Thanks to technology developed by Vadim Cherezov, now of University of Southern California, Leung and her colleagues were able for the first time to form crystals (neatly lined-up groupings) of the TH transmembrane portion and use x-ray crystallography at the Northeastern Collaborative Access Team 24ID-E and 24ID-C x-ray beamlines at the APS, and the 7-1, 11-1, and 12-2 beamlines at the Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource (SSRL) at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory to determine its structure to an atomic-level resolution of 2.8 angstroms (280 trillionths of a meter). Both the APS and the SSRL are Office of Science user facilities.
The team also was able to grow crystals of the whole TH enzyme. These yielded a much lower-resolution structural image, but the researchers were able to enhance the resolution to 6.9 angstroms by plugging in data from crystallography of individual TH portions. In a further study, Professor Bridget Carragher and colleagues at the TSRI-based National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy (NRAMM) imaged individual copies of the enzyme to 18 angstroms using electron microscopy. The electron microscopy data confirmed that TH naturally exists as a “dimer”—two identical copies bound together—and provided major clues to how TH manages to work in this conformation.
Directly above TH’s transmembrane structure, just inside the mitochondrial matrix, is the “domain III” structure that binds NADPH’s precursor molecule, NADP+, during conversion to NADPH. Structural biologists haven’t understood how two such structures could work side by side in the TH dimer and not interfere with each other’s activity. The new structural data suggest that these side-by-side structures are highly flexible and always have different orientations.
“Our most striking finding was that the two domain III structures are not symmetric—one of them faces up while the other faces down,” said Leung.
In particular, one of structures is oriented apparently to catalyze the production of NADPH, while the other is turned towards the membrane, perhaps to facilitate transit of a proton. The new structural model suggests that with each proton transit, the two domain III structures flip and switch their functions. “We suspect that the passage of the proton is what somehow causes this flipping of the domain III structures,” said Leung.
But much work remains to be done to determine TH’s precise structure and mechanism. For example, the new structural data provide evidence of a likely proton channel in the TH transmembrane region, but show only a closed conformation of that structure. “We suspect that this channel can have another, open conformation that lets the proton pass through, so that’s one of the details we want to study further,” said Leung.
“There are many experiments to follow,” Stout said.
See: Josephine H. Leung1, Lici A. Schurig-Briccio2, Mutsuo Yamaguchi1, Arne Moeller1‡, Jeffrey A. Speir1, Robert B. Gennis2, Charles D. Stout1*, “Division of labor in transhydrogenase by alternating proton translocation and hydride transfer,” Science 347(6218), 178 (9 January 2015). DOI: 10.1126/science.1260451
Author affiliations: 1The Scripps Research Institute, 2University of Illinois ‡Present address: Aarhus University
Correspondence: *[email protected]
This research was funded by National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant 5R01GM061545 2004-2008 and by National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS) grant 1R01GM103838-01A1, GM095600 (to R.B.G). The work was performed at the National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy, which is supported by a grant from the NIH NIGMS (P41GM103310). A. Moeller is supported by NIH grant GM073197. The Northeastern Collaborative Access Team beamlines are supported by a grant from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (P41 GM103403) from the National Institutes of Health. This research used resources of the Advanced Photon Source, a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science User Facility operated for the DOE Office of Science by Argonne National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357.
Argonne National Laboratory is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.