The original Columbia University Data Science Institute press release by Kim Martineau can be read here.
Note: First author Kirsten M.Ø. Jensen was recently announced as the winner of this year's European Powder Diffraction Conference (EPDIC) Award for Young Scientists for her work using the atomic pair distribution function (PDF) analysis to characterize nanoparticles, with significant proportions of this work being undertaken at 11-ID-B.
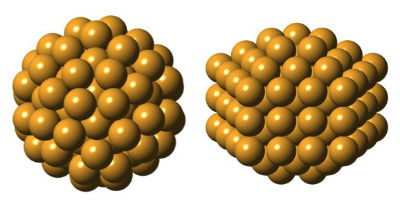
Chemically the same, graphite and diamonds are as physically distinct as two minerals can be, one opaque and soft, the other translucent and hard. What makes them unique is their differing arrangement of carbon atoms. Polymorphs, or materials with the same composition but different structures, are common in bulk materials. Now a new study in Nature Communications that describes results from studies at synchrotron x-ray light sources, including two U.S. Department of Energy user research facilities, confirms they exist in nanomaterials, too.
Researchers in this study from Columbia University, Brookhaven National Laboratory, Colorado State University, and the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility describe two unique structures for the iconic gold nanocluster Au144(SR)60, better known as Gold-144, including a version never seen before. Their discovery gives engineers a new material to explore, along with the possibility of finding other polymorphic nanoparticles.
“This took four years to unravel,” said Simon Billinge, a physics professor at Columbia Engineering and a member of the Data Science Institute. “We weren’t expecting the clusters to take on more than one atomic arrangement. But this discovery gives us more handles to turn when trying to design clusters with new and useful properties.”
Gold has been used in coins and jewelry for thousands of years for its durability, but shrink it to a size 10,000 times smaller than a human hair, and it becomes wildly unstable and unpredictable. At the nanoscale, gold likes to split apart other particles and molecules, making it a useful material for purifying water, imaging and killing tumors, and making solar panels more efficient, among other applications.
Though a variety of nanogold particles and molecules have been made in the lab, very few have had their secret atomic arrangement revealed. But recently, new technologies are bringing these miniscule structures into focus.
Under one approach, high-energy x-ray beams are fired at a sample of nanoparticles. Advanced data analytics are used to interpret the x-ray scattering data and infer the sample’s structure, which is key to understanding how strong, reactive or durable the particles might be.
The PDF method is growing in power and impact due to methodolical advances such as the development of the 11-ID-B beamline at APS. To test the PDF method, Billinge asked chemists at the Colorado State University to make tiny samples of Gold-144,a molecule-sized nanogold cluster first isolated in 1995. Its structure had been theoretically predictedin 2009, and though never confirmed, Gold-144 has found numerous applications, including in tissue-imaging.
Hoping the test would confirm Gold-144’s structure, they analyzed the clusters at the X-ray Science Division beamline 11-ID-B at the Advanced Photon Source (APS) at Argonne National Laboratory, at the X7B beamline and the X17A beamline, both at the National Synchrotron Light Source (NSLS) facility at Brookhaven National Laboratory, and at the European Synchrotron Radiation Source in Grenoble, France, and used the PDF method to infer their structure. Both the APS and NSLS are Office of Science user facilities.
To their surprise, they found an angular core, and not the sphere-like icosahedral core predicted. When they made a new sample and tried the experiment again, this time using synchrotrons at Brookhaven and Argonne national laboratories, the structure came back spherical.
“We didn’t understand what was going on, but digging deeper, we realized we had a polymorph,” said study coauthor Kirsten Jensen, formerly a postdoctoral researcher at Columbia, now a chemistry professor at the University of Copenhagen.
Further experiments confirmed the cluster had two versions, sometimes found together, each with a unique structure indicating they behave differently. The researchers are still unsure if Gold-144 can switch from one version to the other or, what exactly, differentiates the two forms.
To make their discovery, the researchers solved what physicists call the nanostructure inverse problem. How can the structure of a tiny nanoparticle in a sample be inferred from an x-ray signal that has been averaged over millions of particles, each with different orientations?
“The signal is noisy and highly degraded,” said Billinge. “It’s the equivalent of trying to recognize if the bird in the tree is a robin or a cardinal, but the image in your binoculars is too blurry and distorted to tell.”
“Our results demonstrate the power of PDF analysis to reveal the structure of very tiny particles,” added study coauthor Christopher Ackerson, a chemistry professor at Colorado State. "I’ve been trying, off and on, for more than 10 years to get the single-crystal x-ray structure of Gold-144. The presence of polymorphs helps to explain why this molecule has been so resistant to traditional methods."
The PDF approach is one of several rival methods being developed to bring nanoparticle structure into focus. Now that it has proven itself, it could help speed up the work of describing other nanostructures.
The eventual goal is to design nanoparticles by their desired properties, rather than through trial and error, by understanding how form and function relate. Databases of known and predicted structures could make it possible to design new materials with a few clicks of a mouse.
The study is a first step.
“We've had a structure model for this iconic gold molecule for years and then this study comes along and says the structure is basically right but it's got a doppelgänger," said Robert Whetten, a professor of chemical physics at the University of Texas, San Antonio, who led the team that first isolated Gold-144. "It seemed preposterous, to have two distinct structures that underlie its ubiquity, but this is a beautiful paper that will persuade a lot of people.”
See: Kirsten M.Ø. Jensen1, Pavol Juhas2, Marcus A. Tofanelli3, Christine L. Heinecke3, Gavin Vaughan4, Christopher J. Ackerson3*, and Simon J.L. Billinge1,2**, “Polymorphism in magic-sized Au144(SR)60 clusters,” Nat. Commun. 7, 11859 (14 June 2016). DOI: 10.1038/ncomms11859
Author affiliations: 1Columbia University, 2Brookhaven National Laboratory, 3Colorado State University, 4European Synchrotron Radiation Facility
Correspondence: *[email protected], **[email protected].
K.M.Ø.J. acknowledges support from the Villum Foundation. S.J.L.B and P.J. acknowledge funding from Laboratory Directed Research and Development Program 12-007 (Complex Modeling) at Brookhaven National Laboratory, which is funded by the U.S. Department of Energy-Basic Energy Sciences (DOE-BES) grant DE-SC00112704. C.J.A., M.A.T. and C.L.H. acknowledge funding from Colorado State University. C.J.A. was an American Federation for Aging Research New Investigator, while this research was conducted. C.J.A. acknowledges NIH R21 EB014520. Use of the National Synchrotron Light Source, Brookhaven National Laboratory, was supported by the U.S. DOE Office of Science-BES, under contract number DE-AC02-98CH10886. This research used resources of the Advanced Photon Source, a U.S. DOE Office of Science User Facility operated for the U.S. DOE Office of Science by Argonne National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357.
Argonne National Laboratory is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.